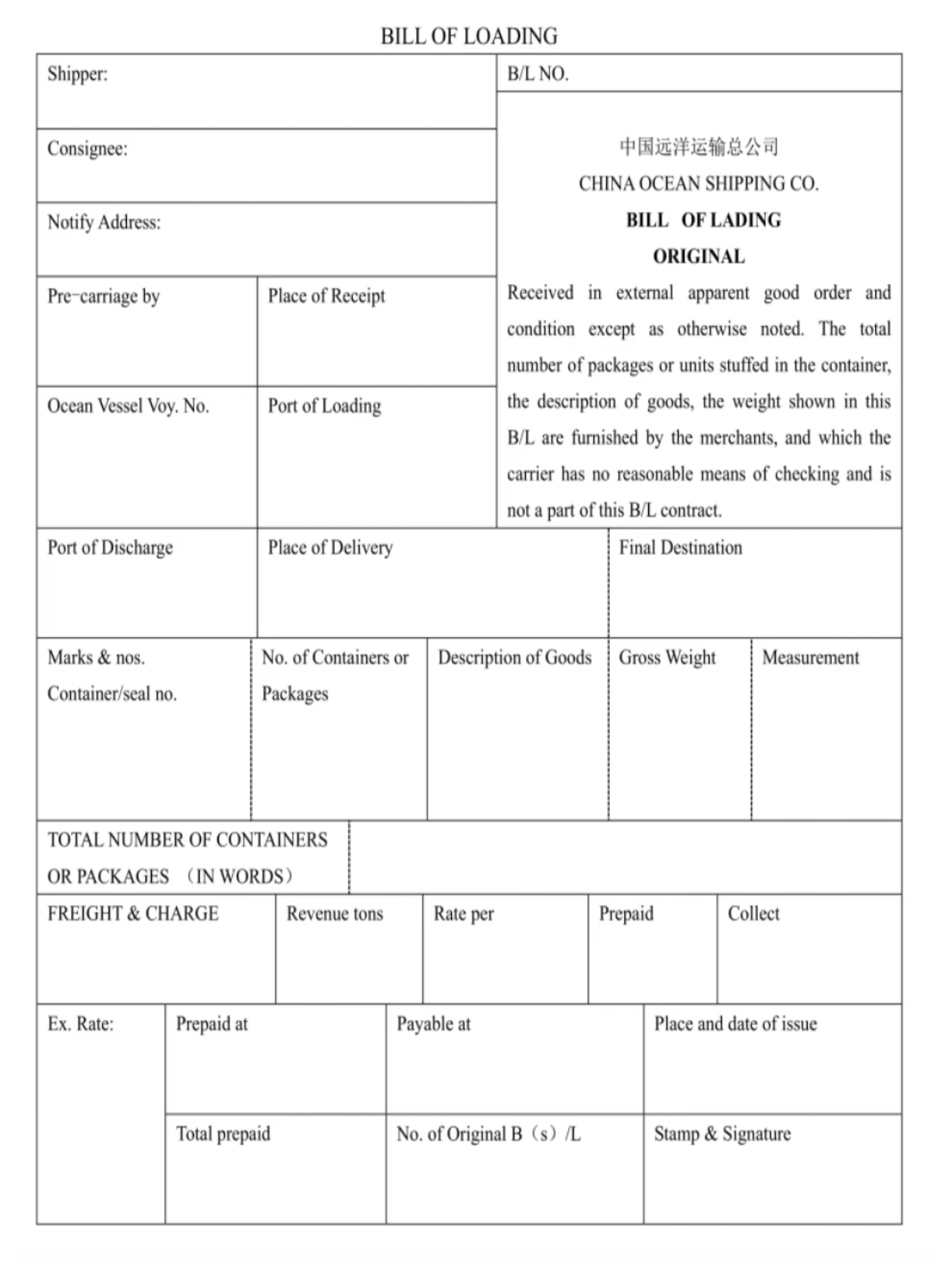
A Bill of Lading (B/L) is a crucial document in international trade and logistics. It is issued by the carrier or its agent as proof that the goods have been received or loaded onto the ship. The B/L serves as a receipt for the goods, a contract for carriage, and a document of title.
Functions of Bill of Lading
Receipt of Goods: The B/L acts as a receipt, confirming that the carrier has received the goods from the shipper. It details the type, quantity, and condition of the goods.
Evidence of Contract of Carriage: The B/L is evidence of the contract between the shipper and the carrier. It outlines the terms and conditions of the transportation, including the route, mode of transport, and freight charges.
Document of Title: The B/L is a document of title, meaning it represents ownership of the goods. The holder of the B/L has the right to take possession of the goods at the destination port. This feature allows the B/L to be negotiable and transferable.
Types of Bill of Lading
Based on Whether the Goods Have Been Loaded:
Shipped on Board B/L: Issued after the goods have been loaded onto the ship. It includes the phrase “Shipped on Board” and the date of loading.
Received for Shipment B/L: Issued when the goods have been received by the carrier but not yet loaded onto the ship. This type of B/L is generally not acceptable under a letter of credit unless specifically allowed.
Based on the Presence of Clauses or Notations:
Clean B/L: A B/L without any clauses or notations that indicate defects in the goods or packaging. It certifies that the goods were in good order and condition when loaded.
Foul B/L: A B/L that includes clauses or notations indicating defects in the goods or packaging, such as “damaged packaging” or “wet goods.” Banks usually do not accept foul B/Ls.
Based on the Consignee’s Name:
Straight B/L: A B/L that specifies the name of the consignee. The goods can only be delivered to the named consignee and cannot be transferred.
Bearer B/L: A B/L that does not specify cons theignee’s name. The holder of the B/L has the right to take possession of the goods. This type is rarely used due to its high risk.
Order B/L: A B/L that states “To Order” or “To Order of…” in the consignee field. It is negotiable and can be transferred through endorsement. This is the most commonly used type in international trade.
Importance of Bill of Lading
In International Trade: The B/L is a vital document for the seller to prove delivery of goods and for the buyer to take possession of the goods. It is often required by banks for payment under a letter of credit.
In Logistics: The B/L serves as the contract between the shipper and the carrier, outlining their rights and obligations. It is also used for arranging transportation, insurance claims, and other logistics-related activities.
Issuance and Transfer of Bill of Lading
Issuance: The B/L is issued by the carrier or its agent after the goods are loaded onto the ship. The shipper typically requests the issuance of the B/L.
Transfer: The B/L can be transferred through endorsement, especially for order B/Ls. In international trade, the seller usually hands over the B/L to the bank, which then forwards it to the buyer or the buyer’s bank after verifying the documents.
Key Points to Note
Date of B/L: The date of shipment on the B/L must match the requirements of the letter of credit; otherwise, the bank may refuse payment.
Clean B/L: The B/L must be clean unless the letter of credit specifically allows for a foul B/L.
Endorsement: For negotiable B/Ls, proper endorsement is necessary to transfer the title of the goods.
Post time: Jul-08-2025